Predictive Model Control and Intelligent Agent are Used To Optimize The Precision Control of an Electro-Pneumatic Actuator-Based Robotic Bottle Capper
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59535/faase.v2i1.245Keywords:
Improving, Electro Pneumatic, Actuator, Bottle Capper, Intelligent AgentAbstract
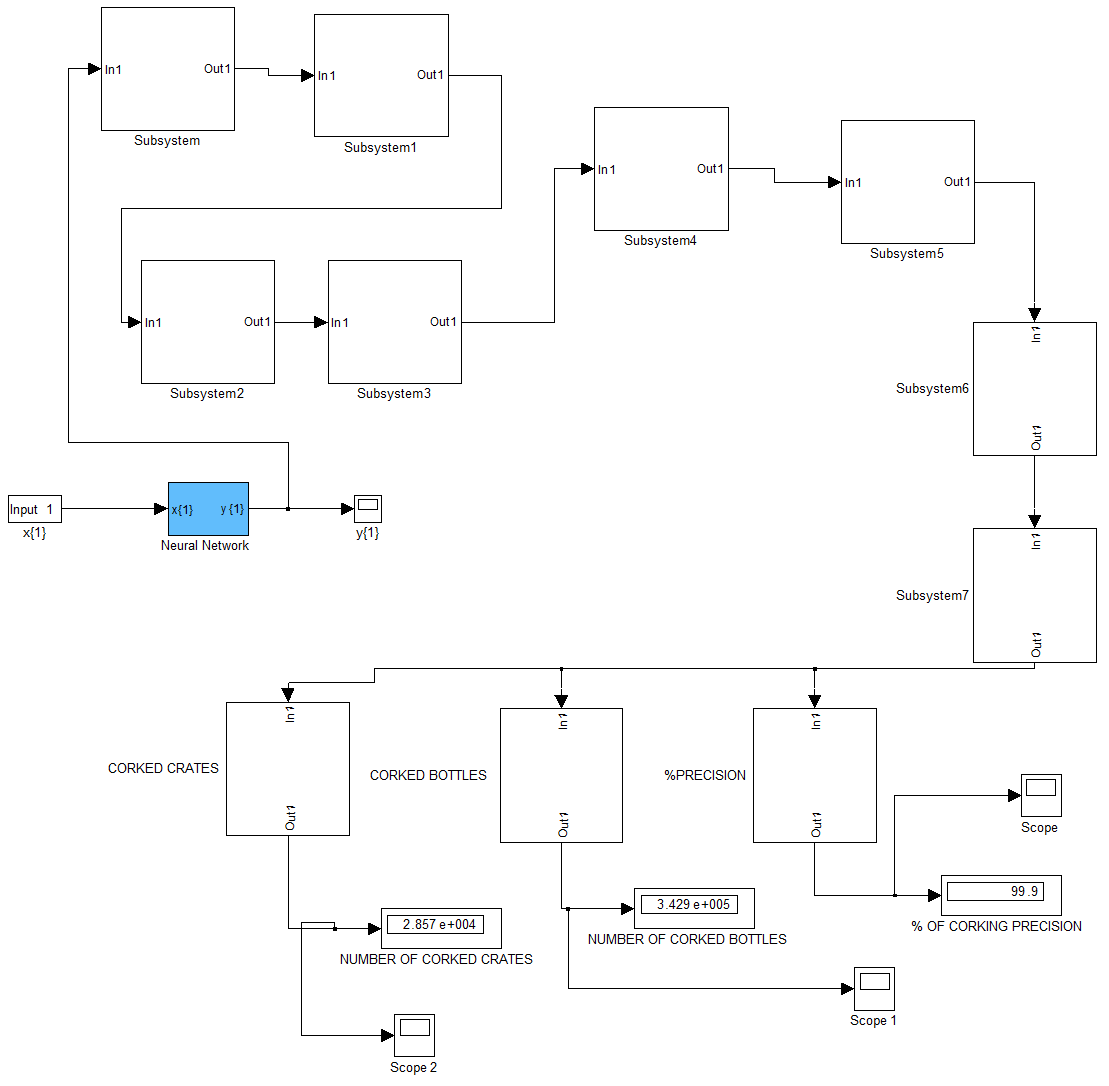
The inferior corking performance observed in bottled drinks from breweries is attributed to poor precision. To address this issue, an enhanced precision control system for an electro-pneumatic actuator-based bottle capper is introduced, utilizing model predictive control and intelligent agent technologies. This involves characterizing the electro-pneumatic actuator system, developing a conventional model for the robotic bottle capper, and designing a rule base to improve precision in the capping mechanism, thereby boosting production capacity per unit time. To achieve this, AI is trained to design a rule-based model ensuring optimal efficacy of the capping mechanism, thus enhancing the brewery industry's production capacity and revenue generation. A SIMULINK model is developed to demonstrate the improved precision control of the electro-pneumatic actuator robotic bottle capper using model predictive control and intelligent agent. Results show a significant increase in corking precision from 94.4% with conventional methods to 99.9% when intelligent agents are incorporated into the system. This translates to a 5.5% improvement in corking precision, with production capacity increasing from 27,000 crates using conventional methods to 28,570 with model predictive control. Moreover, with the integration of intelligence, the production capacity further rises to 342,500 bottles.
Downloads
References
Y. Shi and K. Zhang, ‘Advanced model predictive control framework for autonomous intelligent mechatronic systems: A tutorial overview and perspectives’, Annual Reviews in Control, vol. 52, pp. 170–196, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2021.10.008.
M. Mohtasham Moein et al., ‘Predictive models for concrete properties using machine learning and deep learning approaches: A review’, Journal of Building Engineering, vol. 63, p. 105444, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105444.
Y. Yao and D. K. Shekhar, ‘State of the art review on model predictive control (MPC) in Heating Ventilation and Air-conditioning (HVAC) field’, Building and Environment, vol. 200, p. 107952, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.107952.
Z. Zuo et al., ‘MPC-Based Cooperative Control Strategy of Path Planning and Trajectory Tracking for Intelligent Vehicles’, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 513–522, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1109/TIV.2020.3045837.
S. Peicheng, L. Li, X. Ni, and A. Yang, ‘Intelligent Vehicle Path Tracking Control Based on Improved MPC and Hybrid PID’, IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 94133–94144, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3203451.
T. Li, A. Badre, H. D. Taghirad, and M. Tavakoli, ‘Neural Network Learning of Robot Dynamic Uncertainties and Observer-based External Disturbance Estimation for Impedance Control *’, in 2023 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Jun. 2023, pp. 591–597. doi: 10.1109/AIM46323.2023.10196132.
G. Zhang, Y. Chen, W. Zhou, C. Chen, and Y. Liu, ‘Bioenergy-Based Closed-Loop Medical Systems for the Integration of Treatment, Monitoring, and Feedback’, Small Science, vol. 3, no. 10, p. 2300043, 2023, doi: 10.1002/smsc.202300043.
H. Nasiri and M. M. Ebadzadeh, ‘MFRFNN: Multi-Functional Recurrent Fuzzy Neural Network for Chaotic Time Series Prediction’, Neurocomputing, vol. 507, pp. 292–310, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.08.032.
M. Zhao, J. Wan, and C. Peng, ‘Generalized predictive control using improved recurrent fuzzy neural network for a boiler-turbine unit’, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 121, p. 106053, May 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106053.
Z. Wen, L. Xie, Q. Fan, and H. Feng, ‘Long term electric load forecasting based on TS-type recurrent fuzzy neural network model’, Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 179, p. 106106, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.epsr.2019.106106.
W. Retnaraj, S. Sengupta, T. Q. Dinh, and J. J. Chong, ‘Modeling and Feedback Linearization of an Electric Hovercraft for Path Tracking’, in 2022 25th International Conference on Mechatronics Technology (ICMT), Nov. 2022, pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICMT56556.2022.9997746.
L. Yan, B. Ma, and W. Xie, ‘Robust practical tracking control of an underactuated hovercraft’, Asian Journal of Control, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 2201–2213, 2021, doi: 10.1002/asjc.2585.
A. R. periyanayagam and Y. H. Joo, ‘Integral sliding mode control for increasing maximum power extraction efficiency of variable-speed wind energy system’, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, vol. 139, p. 107958, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2022.107958.
B. Sahoo, S. Keshari Routray, and P. Kumar Rout, ‘Execution of robust dynamic sliding mode control for smart photovoltaic application’, Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, vol. 45, p. 101150, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2021.101150.
O. Jorg and G. Fantoni, ‘A self-adaptive high precision gripper for shape variant components: Towards higher reliability and efficiency of a cobotic cell’, Journal of Manufacturing Systems, vol. 70, pp. 113–126, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2023.04.003.
Q. Zhou, M. Li, C. Fu, X. Ren, Z. Xu, and X. Liu, ‘Precise micro-particle and bubble manipulation by tunable ultrasonic bottle beams’, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, vol. 75, p. 105602, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105602.
N.-Y. Zhao, J.-F. Liu, M.-Y. Su, and Z.-B. Xu, ‘Measurement techniques in injection molding: A comprehensive review of machine status detection, molten resin flow state characterization, and component quality adjustment’, Measurement, vol. 226, p. 114163, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.114163.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Jack Chinedu Edeubaka, Francis Ifeanyi Anyasi, Peter Francis Inyang, Prince Ekpenyong Odo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
By submitting a manuscript to Frontier Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (FAASE), the author(s) agree to the following terms:
-
Copyright: The author(s) retain copyright to their work, granting Frontier Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (FAASE) the right to publish it. Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY).
-
License Grant: The CC BY license allows others to share and adapt the work for any purpose, even commercially, provided proper attribution is given to the original author(s) and the source, a link to the Creative Commons license is provided, and any changes made are indicated.
-
Author's Rights: Authors are allowed to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work, with proper acknowledgment of its initial publication in Frontier Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (FAASE).
-
Permissions: Reproduction, posting, transmission, or other distribution or use of the final published article, in whole or in part, requires prior written permission from Frontier Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (FAASE) and the respective author(s).
-
Attribution: Proper attribution must be given to the original author(s) and the source, indicating that the work was originally published in Frontier Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (FAASE) with a link to the published article.
-
No Warranty: The journal and its editorial team make no representations or warranties regarding the accuracy, completeness, or fitness for a particular purpose of the published work.
-
Dispute Resolution: Any disputes arising from the use of the licensed material shall be governed by the laws of [Jurisdiction] without regard to conflicts of law principles.
By submitting a manuscript to FAASE, the author(s) agree to abide by these license terms and grant the necessary rights to Frontier Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (FAASE) for the publication and dissemination of the submitted work.










